Introduction to Uric Acid
Brief Overview of Uric Acid and Its Role in the Body
Purines, substances present in some foods and produced by the body, break down into uric acid as a byproduct. The blood typically dissolves this compound, and the kidneys excrete it through urine. Understanding what are the symptoms of high uric acid levels in the body is essential for the early detection and management of potential health issues. Recognizing these symptoms can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain healthy uric acid levels and prevent complications.
In healthy individuals, uric acid plays a crucial role as an antioxidant, aiding in the protection of blood vessel linings and contributing to overall cardiovascular health. However, when levels rise beyond normal limits, it can lead to various health issues.
We consider uric acid levels high when they exceed 7 mg/dL in men and 6 mg/dL in women. Elevated uric acid levels often result from either overproduction or underexcretion of this compound by the kidneys.
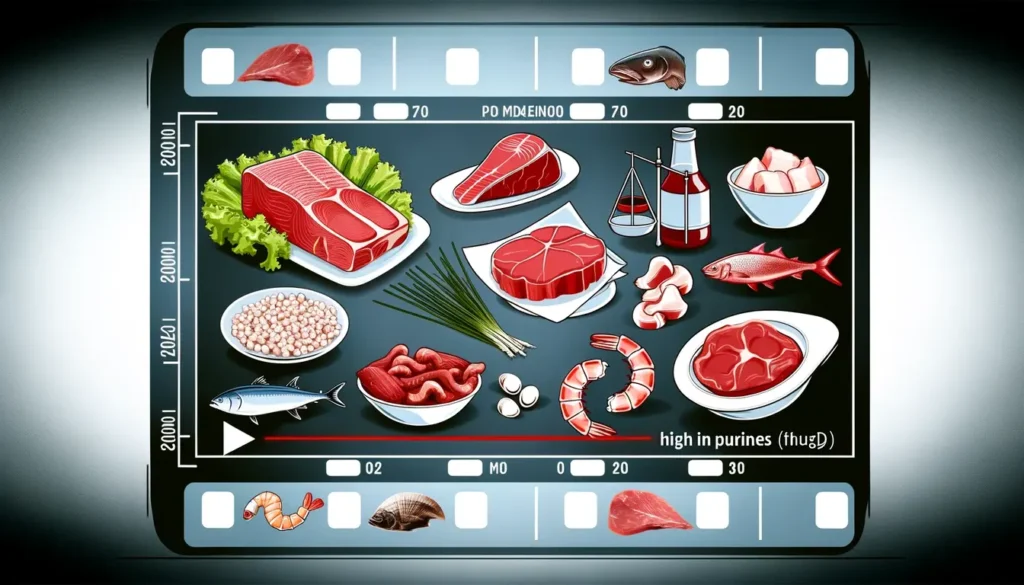
Factors like dietary choices rich in purines (e.g., red meat, seafood), obesity, and kidney dysfunction can increase uric acid levels. The condition where high uric acid levels persist is known as hyperuricemia, serving as a precursor to more severe complications like gout or kidney stones.
Causes of High Uric Acid Levels
High uric acid levels can be indicative of an imbalance within the body’s metabolic processes. Elevated uric acid levels, known as hyperuricemia, occur when the body either produces too much uric acid or excretes too little through the kidneys. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for preventing complications and maintaining optimal health.
Overproduction of Uric Acid
The body breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks, into uric acid. Consuming a diet high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol, can lead to an overproduction of uric acid. Additionally, certain metabolic disorders and genetic factors can cause the body to produce excess uric acid, increasing the risk of hyperuricemia.
Underexcretion of Uric Acid
The kidneys play a vital role in filtering and excreting uric acid from the bloodstream. When the kidneys do not function properly, they may fail to eliminate sufficient amounts of uric acid, leading to its accumulation in the body. Conditions such as chronic kidney disease, dehydration, and certain medications can impair the kidneys’ ability to excrete uric acid effectively.
Lifestyle Factors
Several lifestyle factors can contribute to elevated uric acid levels. Obesity, sedentary habits, and a diet high in sugary beverages and processed foods can increase the risk of hyperuricemia. Managing weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help maintain healthy uric acid levels.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions are associated with high uric acid levels. Metabolic syndrome, characterized by a cluster of conditions such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol levels, can increase uric acid production. Diabetes, hypertension, and hypothyroidism are other conditions that may contribute to elevated uric acid levels.
Genetic Factors
Genetics can play a significant role in an individual’s risk of developing hyperuricemia. A family history of gout or other conditions related to high uric acid levels can indicate a genetic predisposition to hyperuricemia. Understanding one’s genetic risk can aid in early detection and proactive management.
Medications
Certain medications can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate uric acid levels. Diuretics, low-dose aspirin, and medicines for high blood pressure can lead to higher uric acid levels. It is essential to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider, especially if there is a known risk of hyperuricemia.
Importance of Monitoring and Management
Monitoring uric acid levels is crucial for preventing complications such as gout arthritis and kidney stones. Regular blood tests allow for timely intervention to prevent the progression towards more severe symptoms associated with hyperuricemia. Furthermore, high uric acid concentrations may not always present noticeable symptoms initially but could silently contribute to long-term damage if left unaddressed.
By understanding what constitutes high uric acid levels, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing their diet and lifestyle choices and seeking medical advice when necessary. By delving deeper into these thresholds and their implications for overall well-being, one can navigate the potential risks associated with elevated uric acid effectively.
Symptoms of High Uric Acid
Joint Pain: The Telltale Sign of High Uric Acid Levels
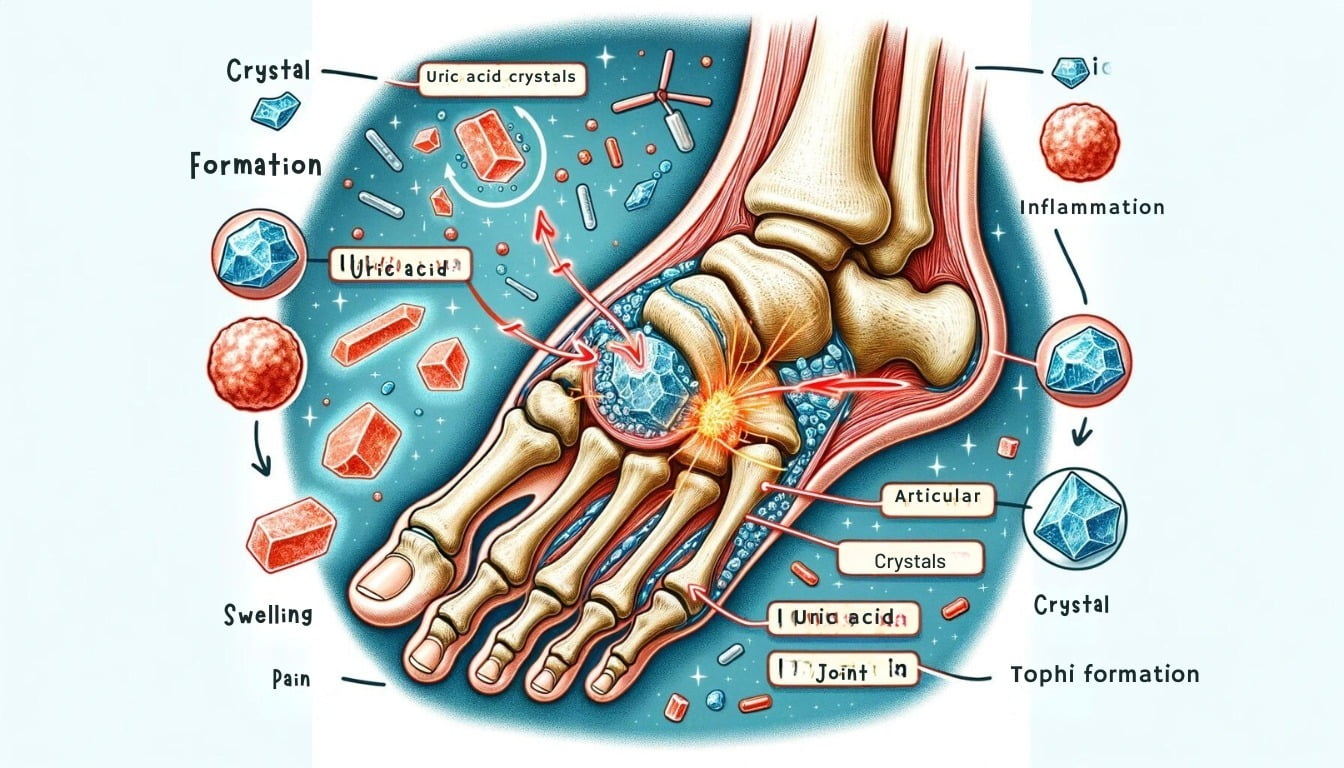
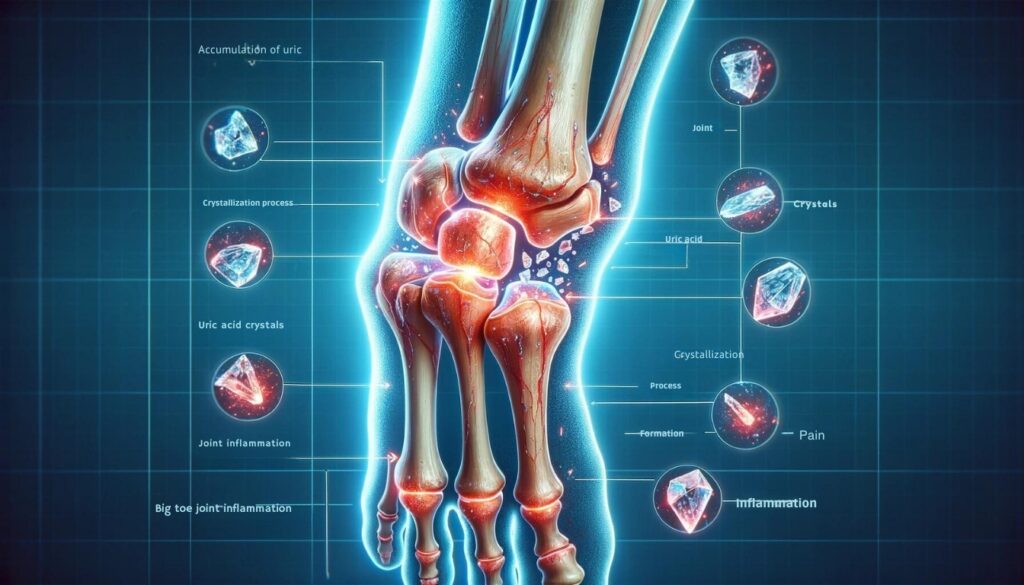
When uric acid levels in the body soar beyond normal range, they can crystallize and deposit in joints, leading to a condition known as gout. These sharp, needle-like crystals form due to elevated uric acid concentrations in the blood, causing inflammation and severe pain.
The crystallization process typically starts with the big toe joint, known as podagra, but can also affect other joints like the knees, ankles, wrists, and fingers. Excruciating pain is frequently associated with gout flare-ups, and the affected area may also experience redness and swelling.
The accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints triggers a cascade of immune responses that exacerbate inflammation and pain. The body perceives these crystals as foreign invaders and launches an attack by releasing inflammatory molecules like cytokines into the affected joint tissues.
Individuals with high uric acid levels experience even more pain as a result of this inflammatory response, which further increases pain and reduces mobility in the affected joint, making simple tasks like walking or even standing incredibly challenging.
Swelling and Inflammation: The Silent Agony of High Uric Acid Levels
Excess uric acid circulating in the bloodstream can lead to chronic low-grade inflammation across the entire body, particularly affecting joints. When high levels of uric acid trigger an inflammatory response in joints, it results in swelling, a common symptom seen in individuals suffering from gout or hyperuricemia.
Increased blood flow to the inflamed area as white blood cells rush to combat perceived threats posed by urate crystals is what causes this swelling. The persistent inflammation associated with high uric acid levels not only causes visible swelling but also contributes to ongoing discomfort and reduced functionality for individuals affected by this condition.
Daily activities that require the movement of inflamed joints become arduous tasks due to both physical pain and psychological distress caused by chronic inflammation. Addressing this underlying cause through appropriate management strategies is crucial for alleviating swelling and restoring mobility for those experiencing the consequences of elevated uric acid levels.

Kidney Issues: Formation of Kidney Stones Due to High Uric Acid Levels
High levels of uric acid in the body can lead to the formation of kidney stones, a painful condition that occurs when crystalized uric acid accumulates in the kidneys. These stones can range in size from tiny granules to larger, obstructive masses, causing significant discomfort and impairing kidney function. The presence of these stones can block the flow of urine within the urinary tract, leading to complications such as urinary tract infections and potential kidney damage if left untreated.
Signs Such as Flank Pain, Blood in Urine, and Frequent Urination
Individuals with high uric acid levels may experience symptoms such as flank pain, which is characterized by a dull ache or sharp discomfort on either side of the abdomen where the kidneys are located. Due to irritation from kidney stones or crystal deposits, this pain can vary in intensity and may accompany blood in the urine (hematuria). Additionally, frequent urination or changes in urine color and odor may indicate underlying kidney issues related to elevated uric acid levels.
Skin Manifestations
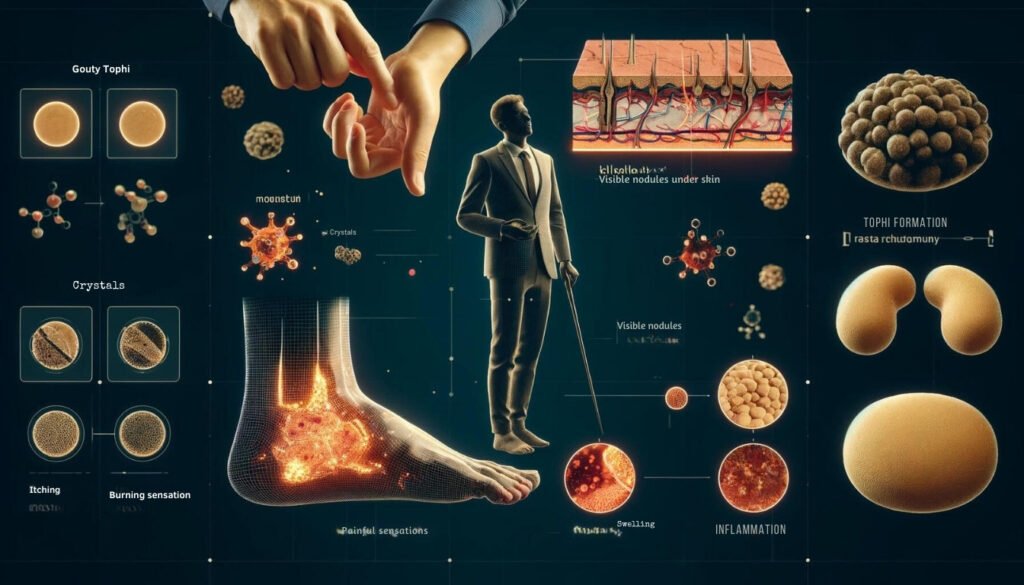
Gouty Tophi: Visible Nodules Under the Skin Filled with Urate Crystals
One distinctive symptom of high uric acid levels manifesting on the skin is the development of gouty tophi. These are visible nodules that form under the skin’s surface and are filled with crystallized urate deposits. Typically found near joints affected by gout, such as fingers, toes, elbows, or ears, these tophi can vary in size and texture.
They often appear whitish or yellowish and may feel firm or gritty when touched. Gouty tophi is not only a cosmetic concern but also an indication of uncontrolled uric acid levels that require medical attention.
Itching or Burning Sensation in Affected Areas
Individuals with high levels of uric acid may experience itching or a burning sensation on their skin where gouty tophi have formed or around joints affected by inflammation due to crystal deposits. This discomfort is often exacerbated during gout attacks, due to increased inflammation and irritation in these areas.
The itching sensation may be persistent and bothersome, impacting daily activities and quality of life for those experiencing this symptom. Proper management of uric acid levels through medication and lifestyle modifications is crucial for alleviating skin-related symptoms associated with hyperuricemia.
Fatigue: The Silent Sign of High Uric Acid Levels
Fatigue, often brushed off as a consequence of a busy lifestyle or lack of sleep, can be a subtle indicator of high uric acid levels in the body. The impact of elevated uric acid on energy levels and overall well-being is profound but often goes unnoticed or attributed to other factors.
When uric acid levels are high, it can lead to increased inflammation in the body, affecting not only joints but also overall energy production. This inflammatory response can manifest as persistent fatigue that may linger despite ample rest.
Moreover, the presence of excess uric acid can disrupt normal metabolic processes within the body, leading to decreased efficiency in energy production at a cellular level. This disruption can leave individuals feeling consistently drained and lacking vitality, even if they maintain healthy lifestyle habits.
It is crucial to recognize that fatigue associated with high uric acid levels is not merely temporary tiredness but a persistent state of low energy that could be indicative of an underlying health issue. Recognizing fatigue as a potential symptom of high uric acid levels is essential for proactive health management.
Do not dismiss fatigue lightly; investigate it further if it persists despite adequate rest and stress management strategies. By understanding the link between elevated uric acid and decreased energy levels, individuals can take steps toward addressing this issue holistically and improving their overall quality of life.
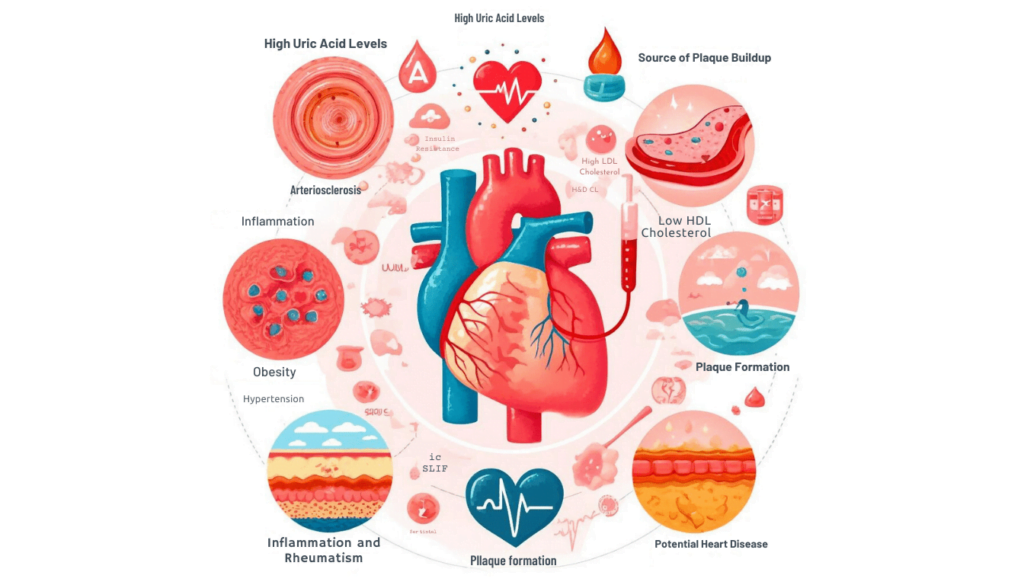
Understanding the Connection Between High Uric Acid Levels and Cardiovascular Health
Elevated levels of uric acid in the body have been increasingly recognized as a potential risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Research indicates that high uric acid levels can contribute to the development of conditions such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, and even heart disease. The mechanism behind this association lies in the ability of uric acid to trigger inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction, all of which are detrimental to cardiovascular health.
Furthermore, studies have shown a correlation between high uric acid levels and an increased risk of developing conditions like stroke and coronary artery disease. Uric acid has been found to promote the formation of plaques in arteries, leading to narrowing and potential blockages that can result in serious cardiac events.
Understanding this link underscores the importance of monitoring uric acid levels as part of comprehensive cardiovascular risk assessment strategies. In addition to its direct impact on cardiovascular health, high uric acid levels may also serve as a marker for underlying metabolic disturbances that further elevate the risk of heart disease.
Conditions such as obesity, insulin resistance, and dyslipidemia are often associated with elevated uric acid levels and can collectively exacerbate cardiovascular risks. Therefore, addressing high uric acid levels not only benefits overall health but also plays a crucial role in preventing cardiovascular complications.
Exploring Potential Links Between High Uric Acid Levels and Mental Health Issues
Recent research has begun to shed light on the intriguing relationship between high uric acid levels and mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety disorders, and cognitive impairment. Researchers are now investigating uric acid for its neuroactive properties and potential impact on brain function, although they have traditionally viewed it as a metabolic byproduct with implications primarily for physical health. Studies suggest that elevated uric acid may contribute to neuroinflammation by activating microglia cells in the brain—a process linked to various psychiatric disorders.
Additionally, hyperuricemia has been associated with changes in neurotransmitter systems like glutamate and dopamine, which play crucial roles in mood regulation and cognitive function. These findings raise intriguing possibilities for exploring targeted interventions that modulate uric acid levels to improve mental well-being.
New research suggests that treating hyperuricemia by making changes to one’s lifestyle or using medications could have benefits beyond improving cardiovascular and metabolic health by also having a positive effect on mental health. By unraveling the complex interplay between high uric acid and its cascading effects on inflammation and neurotransmission, researchers aim to unlock new avenues for holistic approaches toward managing both physical ailments and psychological well-being.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Symptoms Associated with High Uric Acid Levels
The symptoms of high uric acid levels in the body can manifest in various ways. Due to the formation of uric acid crystals, joint pain, particularly in the big toe and knees, is a common indicator. Additionally, individuals may experience kidney issues such as kidney stones, evidenced by flank pain and blood in urine.
Skin manifestations like gouty tophi and itching/burning sensations are also prevalent with elevated uric acid levels. Moreover, do not ignore less-known symptoms such as fatigue, which can serve as subtle cues
Importance of Recognizing Symptoms for Early Detection and Management
Early detection of symptoms associated with high uric acid levels is paramount for effective management and prevention of complications such as gout attacks or kidney damage. By being vigilant about these symptoms, individuals can take proactive measures to reduce their uric acid levels through dietary changes, medication, or lifestyle modifications. For more information on how to manage uric acid levels through diet, read our article, Which Foods Should I Avoid to Maintain Normal Uric Acid Levels? Timely intervention not only alleviates discomfort but also mitigates the long-term consequences associated with untreated hyperuricemia.
Encouragement for Seeking Care
If you suspect that you may be experiencing symptoms related to high uric acid levels, do not hesitate to seek medical attention. Consulting a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance on managing your condition is crucial for your well-being.
Remember that knowing about these symptoms and their significance empowers you to take charge of your health journey. By addressing high uric acid levels proactively, you pave the way toward a healthier future filled with vitality and optimal wellness.
FAQs:
What is uric acid, and how is it produced in the body?
Uric acid is a waste product formed when the body breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks. Typically, the kidneys dissolve it in the blood and excrete it through urine.
What are the common symptoms of high uric acid levels in the body?
Common symptoms include joint pain and inflammation (often in the big toe), kidney stones, skin manifestations like gouty tophi, and fatigue.
How can I know if I have high uric acid levels?
High uric acid levels can be diagnosed through blood tests. Regular monitoring is essential, especially if you have risk factors like a diet high in purines, obesity, or a family history of gout.
What causes high uric acid levels?
High uric acid levels can result from overproduction or underexcretion of uric acid, dietary factors, certain medical conditions (like kidney disease), genetic factors, and certain medications.
Can diet affect uric acid levels?
Yes, consuming foods high in purines (such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol) can increase uric acid levels. A balanced diet low in purines can help manage uric acid levels.
What is hyperuricemia?
Hyperuricemia is a condition characterized by high levels of uric acid in the blood. It can lead to gout, kidney stones, and other health issues if left untreated.
How is high uric acid treated?
Treatment may include medications to reduce uric acid levels, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications such as increasing water intake and reducing purine-rich foods.
Can high uric acid levels cause long-term damage?
If left untreated, high uric acid levels can cause chronic joint pain and damage, kidney stones, and other complications. Early detection and management are crucial.
Are there any preventive measures for high uric acid levels?
Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, managing weight, and regular medical check-ups to monitor uric acid levels.
When should I see a doctor about high uric acid levels?
You should consult a doctor if you experience symptoms like severe joint pain, swelling, or signs of kidney stones, or if you have a family history of gout or other related conditions.